Bitcoin for dummies sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
In this guide, we’ll break down what Bitcoin is, how it works, and why it has become a revolutionary form of digital currency. You’ll learn about its origins, how transactions are processed, and the innovative technology of blockchain that powers it. Whether you’re a complete beginner or just curious about Bitcoin, this overview will provide you with the essential knowledge you need to navigate the world of cryptocurrency.
Introduction to Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that enables peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. It operates on a technology called blockchain, which is a public ledger that records all transactions made with Bitcoin. This revolutionary concept allows for secure and transparent transactions, making it a popular choice for many users worldwide.Bitcoin was created in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto.
The idea was born out of the 2008 financial crisis, where trust in traditional financial institutions was waning. Since its inception, Bitcoin has evolved significantly, witnessing substantial growth in value and popularity, leading to the emergence of thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies.
Key Features of Bitcoin
Several distinctive features set Bitcoin apart from traditional currencies. Understanding these characteristics is essential for grasping the potential of Bitcoin in the financial landscape.
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network. No single entity controls the currency, which enhances security and reduces the risk of manipulation.
- Limited Supply: There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins in existence, a feature that creates scarcity and helps to prevent inflation, similar to precious metals.
- Security: Bitcoin transactions are secured using cryptography, making them nearly impossible to counterfeit. Every transaction is recorded on a blockchain, providing transparency and accountability.
- Global Accessibility: Bitcoin can be sent or received anywhere in the world, making it an ideal option for cross-border transactions without hefty fees or delays associated with traditional banking systems.
- Anonymity: While Bitcoin transactions are public, the identities of those involved are shielded behind cryptographic addresses, offering a level of privacy that is not typically available with traditional banking transactions.
How Bitcoin Works
Bitcoin operates as a decentralized digital currency, relying on complex technology to facilitate secure transactions without the need for traditional banking systems. Understanding how Bitcoin works involves delving into the mechanisms behind transactions, the revolutionary blockchain technology, and the process of mining that generates new Bitcoins.
Bitcoin Transactions and Verification
When a user initiates a Bitcoin transaction, the process begins with the transmission of this transaction to a network of nodes—computers that maintain the Bitcoin blockchain. Each transaction includes details such as the sender’s and receiver’s Bitcoin addresses and the amount being transferred. To ensure the transaction is legitimate, it undergoes a verification process by the network’s nodes. The verification process involves checking the sender’s digital signature and ensuring they have sufficient funds.
Once verified, the transaction is grouped with other transactions into a block. This block is then broadcasted to the network, where miners will compete to add it to the blockchain.
Blockchain Technology
At the core of Bitcoin’s functionality lies blockchain technology. A blockchain is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a reference to the previous block, forming an unalterable chain of data.The significance of blockchain technology is multifaceted:
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to anyone on the network, promoting trust among users.
- Security: The decentralized nature of the blockchain makes it resistant to tampering and fraud.
- Consensus Mechanism: The network reaches an agreement on the validity of transactions through processes like proof of work, ensuring that all copies of the blockchain remain synchronized.
Mining and Bitcoin Generation
Mining is the process by which new Bitcoins are created and transactions are validated on the Bitcoin network. It involves solving complex mathematical problems that require significant computational power. Miners use specialized hardware to compete in solving these problems, known as proof of work.Upon successfully mining a block, the miner is rewarded with a predetermined number of Bitcoins, which incentivizes the maintenance and security of the network.
The mining reward is halved approximately every four years in an event known as the “halving,” which helps control Bitcoin’s supply and simulate scarcity.Mining also plays a crucial role in the verification process, as it secures the network against attacks and ensures that transactions are confirmed and added to the blockchain. As more miners join the network, the difficulty of solving these mathematical problems increases, ensuring that new Bitcoins are generated at a stable rate.
Getting Started with Bitcoin
Setting up your journey into the world of Bitcoin can seem daunting, but with a clear step-by-step guide, you can navigate through the initial stages with ease. This section will cover how to set up a Bitcoin wallet, various methods to purchase Bitcoin, and tips for securing your holdings.
Setting Up a Bitcoin Wallet
A Bitcoin wallet is essential for storing and managing your Bitcoin. The setup process is straightforward and can be done in a few simple steps.
1. Choose a Wallet Type
There are several types of wallets to consider:
Software Wallets
Applications that can be installed on your computer or mobile device.
Hardware Wallets
Physical devices that securely store your private keys offline.
Web Wallets
Online services that allow you to access your Bitcoin from anywhere.
2. Download or Purchase the Wallet
Depending on the type of wallet you choose, download the software or purchase the hardware device from a reputable vendor.
3. Create a New Wallet
Follow the wallet’s instructions to create a new account. This typically involves generating a new address and setting a secure password.
4. Backup Your Wallet
Most wallets will provide a recovery phrase. Write this down and store it in a safe place, as it will be crucial for recovering your wallet if you lose access.
5. Secure Your Wallet
Enable any additional security features offered by your wallet, such as two-factor authentication.
Methods to Buy Bitcoin
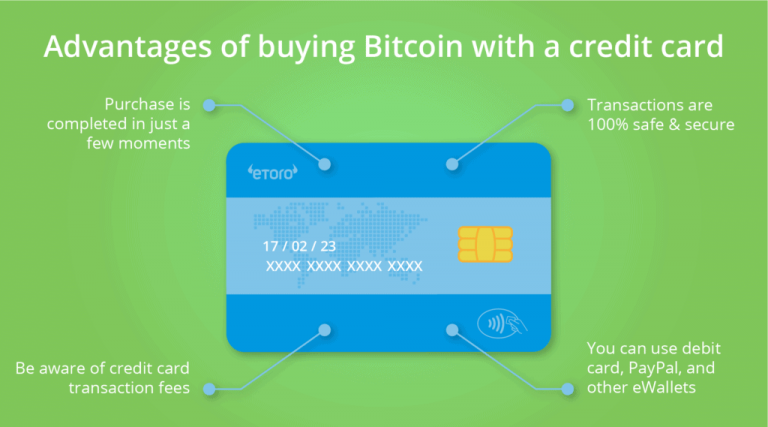
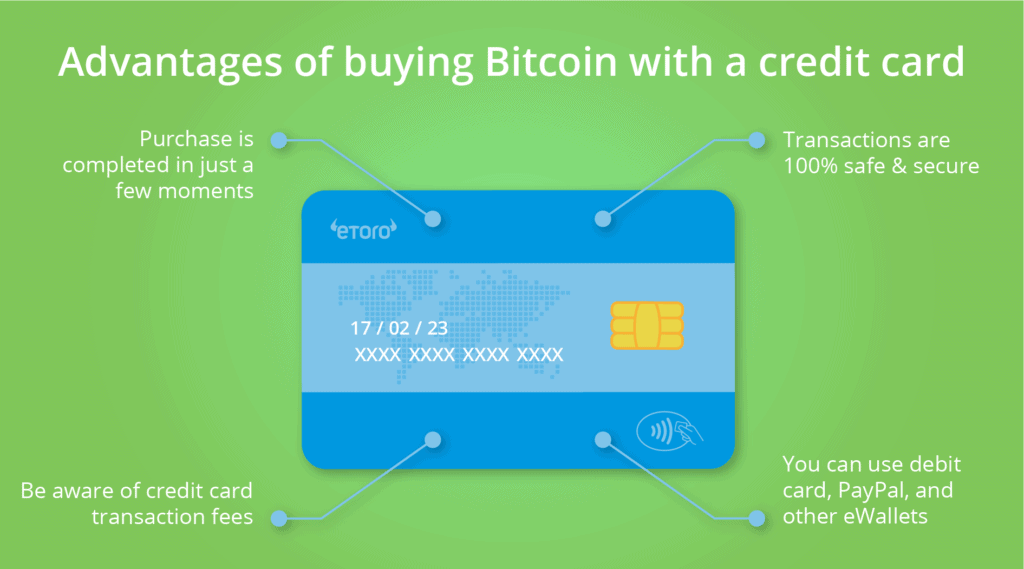
There are various ways to purchase Bitcoin, each with its own advantages and considerations. Understanding these methods can help you choose the best option for your needs. Exchanges: Cryptocurrency exchanges are platforms where you can buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin. Some popular exchanges include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken. To buy Bitcoin through an exchange, you typically need to:
- Create an account and verify your identity.
- Link your bank account or credit card.
- Choose the amount of Bitcoin you wish to purchase and complete the transaction.
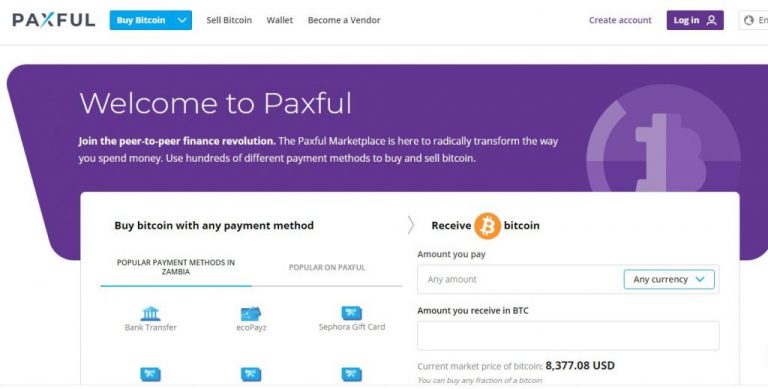
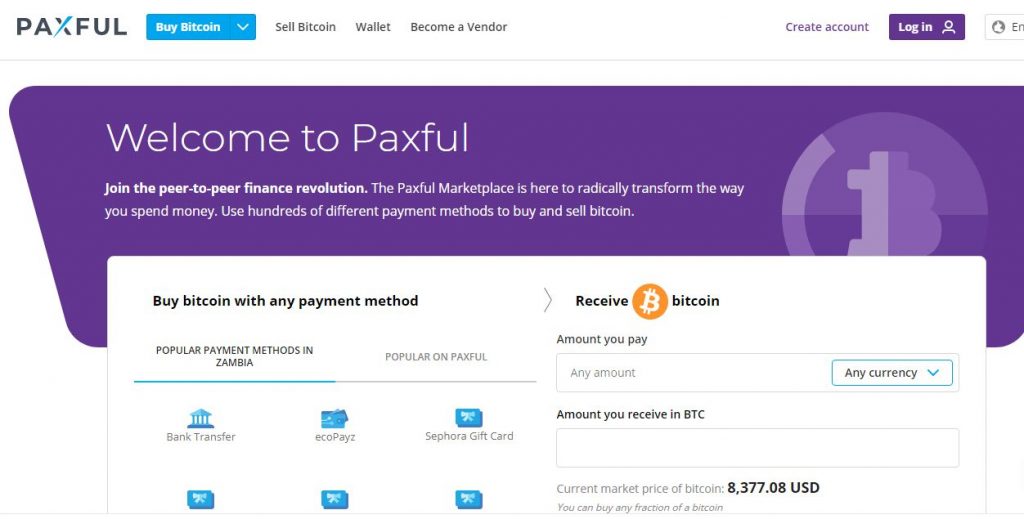
Peer-to-Peer Options: Peer-to-peer (P2P) exchanges facilitate direct transactions between users. Platforms like LocalBitcoins and Paxful allow buyers and sellers to connect without intermediaries. Here’s how it generally works:
- Sign up on a P2P platform and create a profile.
- Browse listings of Bitcoin sellers and find a suitable deal.
- Agree on the terms and complete the transaction directly with the seller.
Securing Bitcoin Holdings
Security is paramount when it comes to holding Bitcoin. Implementing robust security measures can help protect your assets from theft or loss. Consider the following tips:
Use Strong Passwords
Create complex passwords that are hard to guess. Avoid using personal information.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Adding an extra layer of security, 2FA requires not only a password but also a second factor, such as a text message verification.
Keep Software Updated
Regularly update your wallet software and any devices used to access it to protect against vulnerabilities.
Use Cold Storage
For larger amounts of Bitcoin or long-term storage, consider using a hardware wallet or a paper wallet to keep your Bitcoin offline.
Be Cautious of Phishing Scams
Always verify website URLs and avoid clicking on suspicious links that may lead to fraudulent sites.By following these steps and tips, you’ll be well on your way to safely exploring and investing in Bitcoin, equipped with the knowledge to navigate this exciting digital currency landscape.
Using Bitcoin
Bitcoin is not just a digital currency; it’s a versatile tool that can be used for various transactions in the modern economy. As more businesses adopt cryptocurrency, the ways in which Bitcoin can be utilized continue to expand. From purchasing everyday items to investing in technology, understanding how to effectively use Bitcoin is crucial for anyone looking to engage with this revolutionary financial system.One of the most appealing aspects of Bitcoin is its application for purchasing goods and services.
Numerous online and brick-and-mortar stores now accept Bitcoin as a form of payment. Major companies such as Microsoft, Overstock, and AT&T have integrated Bitcoin payments into their checkout systems. These transactions can range from buying electronics to booking travel arrangements. As Bitcoin adoption grows, the list of retailers accepting it continues to lengthen, allowing consumers more freedom in how they shop.
Advantages of Using Bitcoin for Online Transactions
Utilizing Bitcoin for online transactions offers several distinct benefits over traditional payment methods. These advantages can significantly enhance the shopping experience for consumers and businesses alike.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions often have lower fees compared to credit card payments. This can be particularly beneficial for merchants, as they can save on processing costs.
- Speed of Transactions: Bitcoin transactions can be processed quickly, often within minutes. This is especially advantageous for international purchases, where traditional banking methods may take several days.
- Enhanced Security: Bitcoin transactions are secured using cryptographic methods, making them less susceptible to fraud and chargebacks that commonly affect credit card payments.
- Anonymity and Privacy: Bitcoin transactions can be conducted with a level of anonymity that isn’t typically available with traditional banking. While transactions are traceable on the blockchain, personal information is not linked to wallet addresses.
- Global Accessibility: Bitcoin can be used anywhere in the world, providing access to those without traditional banking services. This opens up new markets for businesses and consumers.
Converting Bitcoin to Traditional Currency
Converting Bitcoin to traditional currency is a straightforward process, although it comes with associated fees. Users typically convert Bitcoin through exchanges or peer-to-peer platforms, allowing them to trade their cryptocurrency for fiat currency like USD, EUR, or GBP.The fees for conversion can vary significantly based on the platform used and the transaction amount. It’s important to consider the following aspects when converting Bitcoin:
- Exchange Fees: Most exchanges charge a transaction fee, which can be a flat rate or a percentage of the total value of the transaction. These fees often range from 0.1% to 1% on major exchanges.
- Market Volatility: The value of Bitcoin can fluctuate rapidly, impacting the amount of fiat currency received during conversion. It is advisable to monitor market conditions before making a transaction.
- Withdrawal Fees: Some exchanges charge fees for withdrawing funds after the conversion process, which can vary based on the method chosen (bank transfer, PayPal, etc.).
- Network Fees: Bitcoin transactions incur network fees based on the congestion of the blockchain. Higher network activity can lead to increased fees for faster confirmations.
In summary, using Bitcoin for purchases offers numerous advantages, from lower fees to faster transactions. Converting Bitcoin to traditional currency can be done seamlessly, although users should be aware of the associated fees and market conditions to maximize their benefits.
Bitcoin Investment Strategies

Investing in Bitcoin can be an exhilarating experience, but it also requires a well-thought-out strategy. With its volatile nature, understanding the different approaches to Bitcoin investment can significantly impact your financial journey. This section will explore various investment strategies, each tailored to different risk appetites and investment goals.
Investment Strategies Overview
There are primarily two main strategies for investing in Bitcoin: HODLing and trading. Each strategy has its own set of risks and benefits, making it essential for investors to choose one that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
HODLing vs. Trading
HODLing, a term derived from a misspelled forum post, refers to a long-term investment strategy where investors buy and hold Bitcoin regardless of market fluctuations. On the other hand, trading involves buying and selling Bitcoin over shorter time frames to capitalize on price volatility. Below is a comparison table outlining the risks and benefits associated with these strategies.
| Strategy | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| HODLing |
|
|
| Trading |
|
|
Factors to Consider Before Investing in Bitcoin
Before diving into Bitcoin investments, several critical factors should be evaluated to ensure a sound decision-making process. Consider the following elements:
Market Volatility
Bitcoin’s price can fluctuate dramatically. Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial.
Investment Horizon
Define whether you are looking for short-term gains or long-term wealth accumulation.
Regulatory Landscape
Stay updated on regulatory developments in your country, as they can affect Bitcoin’s legality and market potential.
Security Measures
Implement strong security practices to protect your investment, such as using hardware wallets and two-factor authentication.
Diversification
Consider whether Bitcoin will be part of a more extensive investment portfolio, balancing risks across different asset classes.It is vital for investors to conduct thorough research and possibly consult financial advisors to navigate the intricacies of Bitcoin investment effectively. Each strategy presents unique opportunities and challenges, making informed decision-making essential in this dynamic landscape.
Understanding Bitcoin’s Volatility
Bitcoin is often lauded for its potential to revolutionize finance, but its notorious price volatility can leave both new and seasoned investors scratching their heads. Understanding the reasons behind this volatility is essential for making informed investment decisions. As Bitcoin continues to capture public interest, recognizing its historical trends and the factors that influence its price can provide valuable insights into this digital currency’s behavior.Several factors contribute to the volatility of Bitcoin’s price.
One major reason is its relatively low market capitalization compared to traditional assets like gold or stocks. This means that even small changes in demand or supply can lead to significant price swings. Additionally, Bitcoin’s decentralized nature means that it operates outside traditional financial systems, leading to price fluctuations based on news events, regulatory changes, and market sentiment. Speculation plays a crucial role, as many investors are drawn in by the prospect of high returns, driving prices up or down rapidly.
Historical Price Trends of Bitcoin
Examining historical price trends provides context for Bitcoin’s volatility and reveals patterns that can inform investment strategies. Over the past decade, Bitcoin has experienced multiple boom and bust cycles, attracting attention for its dramatic price increases followed by significant corrections. For example, in late 2017, Bitcoin surged to nearly $20,000 before plummeting to around $3,000 by December 2018. Such fluctuations illustrate the speculative nature of Bitcoin and the emotional responses of investors in reaction to market movements.The implications of these price trends for investors are profound.
Understanding that Bitcoin can experience wild price swings helps investors prepare emotionally and financially for potential losses. Investors should approach Bitcoin with a long-term mindset, recognizing that while the price may be volatile in the short term, it has historically trended upwards over extended periods. This perspective can mitigate the fear of missing out (FOMO) or panic selling during downturns.
Methods for Tracking Bitcoin’s Market Performance
Keeping a pulse on Bitcoin’s market performance is crucial for any investor looking to navigate its volatile landscape. Various tools and platforms can assist in tracking real-time price movements, historical data, and market trends.Many investors rely on cryptocurrency exchanges and financial news websites to monitor Bitcoin prices. These platforms often provide charts that illustrate price movements over different time frames, helping investors spot trends and make informed decisions.
Additionally, price alert systems can notify users when Bitcoin reaches certain price points, allowing for timely buying or selling actions.Another effective method is utilizing market analysis tools that aggregate data from various exchanges to provide an overview of Bitcoin’s liquidity and price variations. These tools can offer insights into market depth, trading volume, and sentiment analysis, allowing investors to gauge overall market conditions.
Moreover, subscribing to financial newsletters or following cryptocurrency analysts on social media can keep investors informed about market developments and expert opinions, further aiding in decision-making. This comprehensive tracking approach can help mitigate risk and harness potential opportunities in the ever-changing Bitcoin market.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
The regulatory landscape for Bitcoin varies greatly across the globe, impacting how individuals and businesses engage with this cryptocurrency. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone involved in Bitcoin trading, investment, or usage, as compliance can significantly influence operations and potential returns.The legal framework surrounding Bitcoin encompasses a range of issues, including how the cryptocurrency is categorized, the regulations that govern its use, and the tax implications for those who trade or hold it.
Different countries have adopted varying approaches, leading to a complex and often confusing environment for users.
Regulatory Landscape of Bitcoin
Many countries are still developing their regulatory approach to Bitcoin. The following are key examples of how various governments handle Bitcoin:
- United States: In the U.S., Bitcoin is classified as a commodity by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and is subject to federal and state regulations. Cryptocurrency exchanges must comply with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) laws.
- European Union: The EU has proposed a framework called the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which aims to create a cohesive regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies across member states. This initiative is still under discussion.
- China: China has taken a strict stance against Bitcoin, banning its trading and mining activities. This policy reflects the government’s concern over financial stability and capital outflow.
- Japan: Japan recognizes Bitcoin as a legal method of payment and has introduced regulatory measures to govern exchanges, ensuring consumer protection and compliance with financial laws.
Tax Implications of Trading and Holding Bitcoin
Taxation is a crucial aspect for anyone trading or holding Bitcoin. The tax treatment of cryptocurrencies varies by jurisdiction but generally follows similar principles. Here are some important points to consider regarding tax implications:
- Capital Gains Tax: In many countries, profits from trading Bitcoin are subject to capital gains tax. This means that if you sell Bitcoin for more than you paid, the profit is taxable.
- Income Tax: If Bitcoin is received as payment for goods or services, it often constitutes ordinary income, and taxes apply based on its fair market value at the time of receipt.
- Reporting Requirements: Many countries require taxpayers to report cryptocurrency holdings and transactions on their tax returns, necessitating meticulous record-keeping.
Comparative Legal Frameworks
The legal frameworks governing Bitcoin differ significantly between countries, reflecting diverse regulatory philosophies and economic priorities. Here are some comparisons:
- Regulatory Clarity: Countries like Japan and Switzerland provide clear regulatory guidelines, fostering innovation and adoption, while others like India and China impose heavy restrictions.
- Consumer Protection: Jurisdictions such as the U.S. and EU emphasize consumer protection through regulations, whereas in countries with less clarity, users may face higher risks of fraud or loss.
- Licensing and Compliance: Some regions require cryptocurrency exchanges to obtain licenses and adhere to strict compliance measures, while in others, no formal licensing is required.
“Understanding the legal and regulatory aspects of Bitcoin is essential for anyone looking to navigate the cryptocurrency landscape safely and successfully.”
The Future of Bitcoin
As Bitcoin continues to gain traction in financial markets and everyday transactions, it’s essential to consider not just its current state but also the future trajectory of this pioneering cryptocurrency. Emerging trends in technology and adoption will play a significant role in shaping Bitcoin’s journey ahead, as will various challenges that may arise. Understanding these dynamics can help investors, users, and enthusiasts prepare for what lies ahead in the evolving landscape of digital currency.
Emerging Trends in Bitcoin Technology and Adoption
The future of Bitcoin is likely to be influenced by several technological advancements and increased adoption rates. As Bitcoin infrastructure develops, new technologies and solutions are expected to emerge. Some of these trends include:
- Layer 2 Solutions: Technologies like the Lightning Network aim to enhance Bitcoin’s scalability and transaction speed, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. This could significantly increase Bitcoin’s use in everyday payments.
- Institutional Adoption: More institutions are integrating Bitcoin into their portfolios, which could lead to greater legitimacy and stability in the market. Companies like Tesla and MicroStrategy have already made significant investments in Bitcoin.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): The rise of DeFi platforms utilizing Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies could revolutionize traditional finance, offering lending, borrowing, and trading options without intermediaries.
- Interoperability: Increased focus on interoperability between different blockchain networks may enhance Bitcoin’s functionality and usability in the wider crypto ecosystem.
Potential Challenges Facing Bitcoin
Despite its promising future, Bitcoin faces several challenges that could hinder its growth and adoption. Analyzing these challenges is crucial for stakeholders:
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Governments worldwide are developing regulations for cryptocurrencies. Stricter regulations could impact Bitcoin’s operation and trading, creating uncertainty for investors.
- Environmental Concerns: Bitcoin mining is often criticized for its high energy consumption. The sustainability debate could lead to calls for more eco-friendly practices or alternative consensus mechanisms.
- Market Volatility: Bitcoin’s price fluctuations can deter potential users and investors. A stable price, along with measures to address volatility, may be necessary for broader adoption.
- Competition from Altcoins: As the cryptocurrency market evolves, Bitcoin may face increased competition from alternative coins that offer unique features or improvements over Bitcoin’s original framework.
Insights on Bitcoin’s Evolution Over the Next Decade
Looking ahead, Bitcoin is poised for significant evolution within the next ten years, driven by technological advancements and market demands. Key insights into this evolution include:
- Increased User Adoption: As knowledge of Bitcoin grows, more individuals and businesses are likely to embrace it, leading to a broader understanding and acceptance of cryptocurrencies in daily transactions.
- Integration with Traditional Finance: With financial institutions exploring blockchain technology, Bitcoin could become integrated into traditional banking services, providing users with seamless access to digital assets.
- Enhanced Security Features: Ongoing improvements in security measures, including quantum resistance, could make Bitcoin transactions safer and more reliable, which is crucial as it gains wider acceptance.
- Global Payment Solutions: Bitcoin’s role as a medium for cross-border transactions may solidify, offering a convenient alternative to traditional remittance services, especially in developing countries.
Common Myths about Bitcoin
Many people have misconceptions about Bitcoin that can lead to confusion and misinformation. Understanding these myths is crucial for anyone looking to engage with or invest in Bitcoin. By debunking these myths, we can demystify Bitcoin and encourage informed discussions about its functionalities and potential.One prevalent misconception is that Bitcoin is primarily used for illegal activities. While it’s true that Bitcoin has been associated with illegal transactions, studies show that the percentage of illicit transactions is declining as the ecosystem matures.
In fact, Bitcoin is often more traceable than cash, making it easier for law enforcement to track illegal activity.
Misunderstood Terms Related to Bitcoin
To further clarify common misconceptions around Bitcoin, it’s helpful to break down some frequently misunderstood terms. These terms often contribute to the myths surrounding Bitcoin and can create barriers to understanding.
- Blockchain: The foundational technology that powers Bitcoin, serving as a public ledger of all transactions. It’s not just a Bitcoin thing; many industries are exploring its potential.
- Wallet: A digital tool that allows users to store, send, and receive Bitcoin. It doesn’t physically hold Bitcoin; rather, it manages the keys necessary to access the blockchain.
- Mining: The process of validating and adding transactions to the blockchain. It’s not just about creating new Bitcoins; it also secures the network.
- Altcoin: Any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Many altcoins aim to improve upon Bitcoin’s technology or address different needs in the market.
- Decentralization: A key feature of Bitcoin, meaning that it operates without a central authority. This can be misunderstood as complete anonymity or lack of governance, which is not entirely accurate.
Understanding these terms can significantly enhance your knowledge of Bitcoin and counteract some of the myths. For instance, many people believe that Bitcoin wallets are unsafe, but the reality is that, with proper security measures, they can be highly secure.
“The beauty of Bitcoin lies in its ability to empower individuals with financial sovereignty.”
Real-life testimonials reveal that many users find Bitcoin to be a secure way to store value and transact. For example, a small business owner shared how accepting Bitcoin increased their customer base and allowed for quicker transactions with lower fees compared to traditional methods. These experiences counter the myth that Bitcoin is too volatile or risky for everyday transactions.Understanding these myths and the reality behind them can pave the way for more informed decisions regarding Bitcoin and its role in the financial landscape.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Bitcoin for dummies not only demystifies the complexities of cryptocurrency but also opens up opportunities for utilizing and investing in this digital asset. As you explore Bitcoin further, remember that understanding its fundamentals can empower you to make informed decisions in this ever-evolving landscape. Embrace the journey and stay curious—who knows what you might discover in the world of Bitcoin!
Helpful Answers
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that allows for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority.
How do I buy Bitcoin?
You can buy Bitcoin through exchanges, direct peer-to-peer transactions, or Bitcoin ATMs.
Is Bitcoin safe to use?
While Bitcoin transactions are secure, users must take precautions such as using wallets and two-factor authentication to protect their holdings.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that records all Bitcoin transactions in a secure and transparent manner.
Can I lose my Bitcoin investment?
Yes, like any investment, Bitcoin carries risks, and prices can be volatile, leading to potential losses.